- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Investigating diagnostic potential of long non-coding RNAs in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma using TCGA database and clinical specimens
Read this article at
Abstract
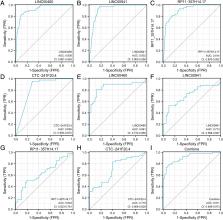
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma (HNSCC) is a prevalent and prognostically challenging cancer worldwide. The role of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in cancer regulation is progressively being understood. This study aims to identify lncRNAs with diagnostic potential as biomarkers for HNSCC. Statistical analysis was performed on expression data from the Cancer Genome Atlas (TCGA) database to identify potential lncRNAs associated with HNSCC. Four selected lncRNAs were validated using real-time quantitative reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction and correlated with clinical factors. Functional roles were further investigated. A total of 488 differentially expressed lncRNAs were identified in TCGA-HNSC. After rigorous evaluation based on p-values, survival analysis, and ROC analysis, 24 lncRNAs were prioritized for additional investigation. LINC00460, LINC00941, CTC-241F20.4, and RP11-357H14.17 were established as candidate diagnostic biomarkers. These lncRNAs exhibited elevated expression in HNSCC tissues and were associated with poor prognosis. Combining them showed high diagnostic accuracy. Notably, LINC00460 and CTC-241F20.4 demonstrated a significant elevation in the advanced stages of HNSCC. We constructed an lncRNA-mRNA regulatory network, and the array of significant regulatory pathways identified included focal adhesion, regulation of epithelial cell migration, and others. Additionally, these lncRNAs were found to influence immune responses by modulating immune cell infiltration in the HNSCC microenvironment. Our research indicates that LINC00460, LINC00941, RP11-357H14.17, and CTC-241F20.4 may have diagnostic and prognostic importance in HNSCC. Furthermore, we have gained insights into their potential functional roles, particularly about immune responses and interactions in the microenvironment.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Pan-cancer Immunogenomic Analyses Reveal Genotype-Immunophenotype Relationships and Predictors of Response to Checkpoint Blockade.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found