- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Novel Role for SIRT-1 in L-Arginine Protection against STZ Induced Myocardial Fibrosis in Rats
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
L-arginine (L-ARG) effectively protects against diabetic impediments. In addition, silent information regulator (SIRT-1) activators are emerging as a new clinical concept in treating diabetic complications. Accordingly, this study aimed at delineating a role for SIRT-1 in mediating L-ARG protection against streptozotocin (STZ) induced myocardial fibrosis.
Methods
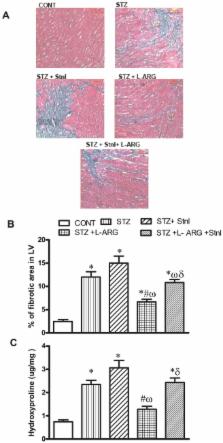
Male Wistar rats were allocated into five groups; (i) normal control rats received 0.1 M sodium citrate buffer (pH 4.5); (ii) STZ at the dose of 60 mg/kg dissolved in 0.1 M sodium citrate buffer (pH 4.5); (iii) STZ + sirtinol (Stnl; specific inhibitor of SIRT-1; 2 mg/Kg, i.p.); (iv) STZ + L-ARG given in drinking water (2.25%) or (v) STZ + L-ARG + Stnl.
Results
L-ARG increased myocardial SIRT-1 expression as well as its protein content. The former finding was paralleled by L-ARG induced reduction in myocardial fibrotic area compared to STZ animals evidenced histopathologically. The reduction in the fibrotic area was accompanied by a decline in fibrotic markers as evident by a decrease in expression of collagen-1 along with reductions in myocardial TGF-β, fibronectin, CTGF and BNP expression together with a decrease in TGF-β and hydroxyproline contents. Moreover, L-ARG increased MMP-2 expression in addition to its protein content while decreasing expression of PAI-1. Finally, L-ARG protected against myocardial cellular death by reduction in NFκ-B mRNA as well as TNF-α level in association with decline in Casp-3 and FAS expressions andCasp-3protein content in addition to reduction of FAS positive cells. However, co-administration of L-ARG and Stnl diminished the protective effect of L-ARG against STZ induced myocardial fibrosis.
Related collections
Most cited references60
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Potential therapeutic targets for cardiac fibrosis: TGFbeta, angiotensin, endothelin, CCN2, and PDGF, partners in fibroblast activation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Redox regulation of SIRT1 in inflammation and cellular senescence.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found