- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The different faces of the macrophage in asthma
Read this article at
Abstract
Purpose of review
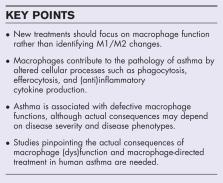
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease in which changes in macrophage polarization have been shown to contribute to the pathogenesis. The present review discusses the contribution of changes in macrophage function to asthma related to polarization changes and elaborates on possible therapeutic strategies targeting macrophage function and polarization.
Recent findings
Macrophage function alterations were shown to contribute to asthma pathology in several ways. One is by impaired phagocytosis and efferocytosis. Another is by changing inflammation, by altered (anti)inflammatory cytokine production and induction of the inflammasome. Finally, macrophages can contribute to remodeling in asthma, although little evidence is present in humans yet.
Novel therapeutic strategies targeting macrophages include dampening inflammation by changing polarization or by inhibiting the NLRP3 inflammasome, and by targeting efferocytosis. However, many of these studies were performed in animal models leaving their translation to the clinic for future research.
Related collections
Most cited references51
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Alum adjuvant boosts adaptive immunity by inducing uric acid and activating inflammatory dendritic cells
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found