- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prevalence of ectoparasite infestations in owned dogs in Kwara State, Nigeria
Read this article at
Abstract
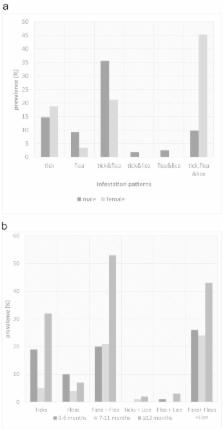
In Nigeria, dogs are the common companions in many households and, harbor wide range of ectoparasites of severe zoonotic potentials. A cross sectional survey was conducted to examine the prevalence, intensity and risk factors of ectoparasite infestation among the owned dogs in Kwara state, Nigeria. A total of 333 dogs were screened for ectoparasites, and questionnaires were applied to obtain information regarding; age, sex, breeds, coat colour and management practices by dog owners. Two hundred and seventy one (81.4%) dogs were infested with at least one species of ectoparasite and multiple infestations recorded mostly among the female dogs. Six species of ectoparasites of three taxa were identified: ticks ( Rhipicephalus sanguineus sensu lato, Haemaphysalis leachii and Amblyomma variegatum), fleas ( Ctenocephalides canis and C. felis) and louse ( Heterodoxus spiniger). R. sanguineus s.l. was the most prevalent (70.3%) followed by C. felis (42.1%) and H. spiniger (30.0%). Intensities of C. felis, H. spiniger and R. sanguineus s.l infestations were significantly higher in female and younger dogs (p < 0.001). Ectoparasites occurrence varied with breed and coat colour of host. A high prevalence of ectoparasite infestation recorded is at variance with the knowledge of dogs' owners in this study area. Therefore, intervention based on provision of veterinary clinics and prevention and management of parasite infestation in endemic area would mitigate the possible health hazard associated with the ectoparasitic infestation of dogs.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The role of companion animals in the emergence of parasitic zoonoses.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Climate Niches of Tick Species in the Mediterranean Region: Modeling of Occurrence Data, Distributional Constraints, and Impact of Climate Change

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found