- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cancer Treatment Using Peptides: Current Therapies and Future Prospects
Read this article at
Abstract
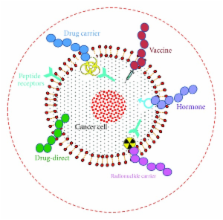
This paper discusses the role of peptides in cancer therapy with special emphasis on peptide drugs which are already approved and those in clinical trials. The potential of peptides in cancer treatment is evident from a variety of different strategies that are available to address the progression of tumor growth and propagation of the disease. Use of peptides that can directly target cancer cells without affecting normal cells (targeted therapy) is evolving as an alternate strategy to conventional chemotherapy. Peptide can be utilized directly as a cytotoxic agent through various mechanisms or can act as a carrier of cytotoxic agents and radioisotopes by specifically targeting cancer cells. Peptide-based hormonal therapy has been extensively studied and utilized for the treatment of breast and prostate cancers. Tremendous amount of clinical data is currently available attesting to the efficiency of peptide-based cancer vaccines. Combination therapy is emerging as an important strategy to achieve synergistic effects in fighting cancer as a single method alone may not be efficient enough to yield positive results. Combining immunotherapy with conventional therapies such as radiation and chemotherapy or combining an anticancer peptide with a nonpeptidic cytotoxic drug is an example of this emerging field.
Related collections
Most cited references144
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Cancer genes and the pathways they control.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Treatment with the radiolabeled somatostatin analog [177 Lu-DOTA 0,Tyr3]octreotate: toxicity, efficacy, and survival.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found