- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Environmental DNA metabarcoding of wild flowers reveals diverse communities of terrestrial arthropods
Read this article at
Abstract
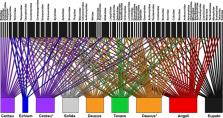
Terrestrial arthropods comprise the most species‐rich communities on Earth, and grassland flowers provide resources for hundreds of thousands of arthropod species. Diverse grassland ecosystems worldwide are threatened by various types of environmental change, which has led to decline in arthropod diversity. At the same time, monitoring grassland arthropod diversity is time‐consuming and strictly dependent on declining taxonomic expertise. Environmental DNA (eDNA) metabarcoding of complex samples has demonstrated that information on species compositions can be efficiently and non‐invasively obtained. Here, we test the potential of wild flowers as a novel source of arthropod eDNA. We performed eDNA metabarcoding of flowers from several different plant species using two sets of generic primers, targeting the mitochondrial genes 16S rRNA and COI. Our results show that terrestrial arthropod species leave traces of DNA on the flowers that they interact with. We obtained eDNA from at least 135 arthropod species in 67 families and 14 orders, together representing diverse ecological groups including pollinators, parasitoids, gall inducers, predators, and phytophagous species. Arthropod communities clustered together according to plant species. Our data also indicate that this experiment was not exhaustive, and that an even higher arthropod richness could be obtained using this eDNA approach. Overall, our results demonstrate that it is possible to obtain information on diverse communities of insects and other terrestrial arthropods from eDNA metabarcoding of wild flowers. This novel source of eDNA represents a vast potential for addressing fundamental research questions in ecology, obtaining data on cryptic and unknown species of plant‐associated arthropods, as well as applied research on pest management or conservation of endangered species such as wild pollinators.
Related collections
Most cited references55
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Environmental DNA for wildlife biology and biodiversity monitoring.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found