- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
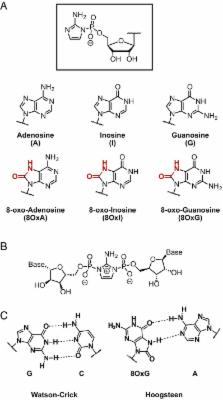
Inosine, but none of the 8-oxo-purines, is a plausible component of a primordial version of RNA
Read this article at
Significance
The RNA world hypothesis assumes the abiotic synthesis of nucleotides, as well as their participation in nonenzymatic RNA replication. Whereas prebiotic syntheses of the canonical purine nucleotides remain inefficient, a prebiotically plausible route to the 8-oxo-purines has been reported. Although these noncanonical purine nucleotides are known to engage in non-Watson–Crick pairing with their canonical purine counterparts, their behavior in nonenzymatic RNA copying has not been evaluated. Our study indicates that none of the 8-oxo-purines behaves as a suitable substrate for nonenzymatic RNA copying. However, inosine turns out to exhibit reasonable rates and fidelities in RNA copying reactions. We propose that inosine could have served as a surrogate for guanosine in the early emergence of life.
Abstract
The emergence of primordial RNA-based life would have required the abiotic synthesis of nucleotides, and their participation in nonenzymatic RNA replication. Although considerable progress has been made toward potentially prebiotic syntheses of the pyrimidine nucleotides (C and U) and their 2-thio variants, efficient routes to the canonical purine nucleotides (A and G) remain elusive. Reported syntheses are low yielding and generate a large number of undesired side products. Recently, a potentially prebiotic pathway to 8-oxo-adenosine and 8-oxo-inosine has been demonstrated, raising the question of the suitability of the 8-oxo-purines as substrates for prebiotic RNA replication. Here we show that the 8-oxo-purine nucleotides are poor substrates for nonenzymatic RNA primer extension, both as activated monomers and when present in the template strand; their presence at the end of a primer also strongly reduces the rate and fidelity of primer extension. To provide a proper comparison with 8-oxo-inosine, we also examined primer extension reactions with inosine, and found that inosine exhibits surprisingly rapid and accurate nonenzymatic RNA copying. We propose that inosine, which can be derived from adenosine by deamination, could have acted as a surrogate for G in the earliest stages of the emergence of life.
Related collections
Most cited references24
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The origin of the genetic code.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Synthesis of activated pyrimidine ribonucleotides in prebiotically plausible conditions.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found