- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
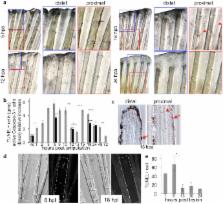
Sustained production of ROS triggers compensatory proliferation and is required for regeneration to proceed
Read this article at
Abstract
A major issue in regenerative medicine is the role of injury in promoting cell plasticity. Here we explore the function of reactive oxygen species (ROS) induced through lesions in adult zebrafish. We show that ROS production, following adult fin amputation, is tightly regulated in time and space for at least 24 hours, whereas ROS production remains transient (2 hours) in mere wound healing. In regenerative tissue, ROS signaling triggers two distinct parallel pathways: one pathway is responsible for apoptosis, and the other pathway is responsible for JNK activation. Both events are involved in the compensatory proliferation of stump epidermal cells and are necessary for the progression of regeneration. Both events impact the Wnt, SDF1 and IGF pathways, while apoptosis only impacts progenitor marker expression. These results implicate oxidative stress in regeneration and provide new insights into the differences between healing and regeneration.
Related collections
Most cited references45
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A tissue-scale gradient of hydrogen peroxide mediates rapid wound detection in zebrafish
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Reactive oxygen species promote TNFalpha-induced death and sustained JNK activation by inhibiting MAP kinase phosphatases.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found