- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The therapeutic and diagnostic potential of regulatory noncoding RNAs in medulloblastoma
Read this article at
Abstract
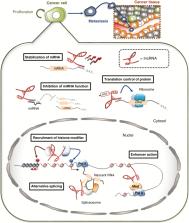
Medulloblastoma, a central nervous system tumor that predominantly affects children, always requires aggressive therapy. Nevertheless, it frequently recurs as resistant disease and is associated with high morbidity and mortality. While recent efforts to subclassify medulloblastoma based on molecular features have advanced our basic understanding of medulloblastoma pathogenesis, optimal targets to increase therapeutic efficacy and reduce side effects remain largely undefined. Noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs) with known regulatory roles, particularly long noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs), are now known to participate in medulloblastoma biology, although their functional significance remains obscure in many cases. Here we review the literature on regulatory ncRNAs in medulloblastoma. In providing a comprehensive overview of ncRNA studies, we highlight how different lncRNAs and miRNAs have oncogenic or tumor suppressive roles in medulloblastoma. These ncRNAs possess subgroup specificity that can be exploited to personalize therapy by acting as theranostic targets. Several of the already identified ncRNAs appear specific to medulloblastoma stem cells, the most difficult-to-treat component of the tumor that drives metastasis and acquired resistance, thereby providing opportunities for therapy in relapsing, disseminating, and therapy-resistant disease. Delivering ncRNAs to tumors remains challenging, but this limitation is gradually being overcome through the use of advanced technologies such as nanotechnology and rational biomaterial design.
Related collections
Most cited references96
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Targeting microRNAs in cancer: rationale, strategies and challenges.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Genome-wide analysis of drosophila circular RNAs reveals their structural and sequence properties and age-dependent neural accumulation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found