- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Treatment With Liraglutide Exerts Neuroprotection After Hypoxic–Ischemic Brain Injury in Neonatal Rats via the PI3K/AKT/GSK3β Pathway
Read this article at
Abstract
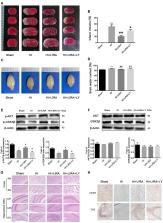
Neonatal hypoxic–ischemic (HI) brain injury is a detrimental disease, which results in high mortality and long-term neurological deficits. Nevertheless, the treatment options for this disease are limited. Thus, the aim of the present study was to assess the role of liraglutide in neonatal HI brain injury in rats and investigate the associated mechanisms. The results showed that treatment with liraglutide significantly reduced infarct volume and ameliorated cerebral edema, decreased inflammatory response, promoted the recovery of tissue structure, and improved prognosis following HI brain injury. Moreover, treatment with liraglutide inhibited apoptosis and promoted neuronal survival both in the rat model and following oxygen-glucose deprivation (OGD) insult. LY294002, an inhibitor of phosphoinositide 3-kinase (PI3K), partially reversed these therapeutic effects, suggesting that the PI3K/protein kinase B (Akt) pathway was involved. In conclusion, our data revealed that treatment with liraglutide exerts neuroprotection after neonatal HI brain injury via the PI3K/Akt/glycogen synthase kinase-3β (GSK3β) pathway and may be a promising therapy for this disease.
Related collections
Most cited references42
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy: a review for the clinician.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The diabetes drug liraglutide prevents degenerative processes in a mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found