- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Experimental study of dye removal from industrial wastewater by membrane technologies of reverse osmosis and nanofiltration
Read this article at
Abstract
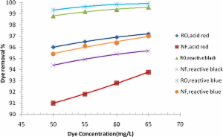
Currently, biological method has been utilized in the treatment of wastewater -containing synthetic dyes used by textile industries in Iraq. The present work was devoted to study the operating feasibility using reverse osmosis (RO) and nanofiltration (NF) membrane systems as an alternative treatment method of wastewater discharged from Iraqi textile mills. Acid red, reactive black and reactive blue dyes were selected, based on the usage rate in Iraq. Effects of dye concentration, pH of solution, feed temperature, dissolved salts and operating pressure on permeate flux and dye rejection were studied. Results at operating conditions of dye concentration = 65 mg/L, feed temperature = 39°C and pressure = 8 bar showed the final dye removal with RO membrane as 97.2%, 99.58% and 99.9% for acid red, reactive black and reactive blue dyes, respectively. With NF membrane, the final dye removal were as 93.77%, 95.67%, and 97% for red, black and blue dyes, respectively. The presence of salt (particularly NaCl) in the dye solution resulted in a higher color removal with a permeate flux decline. It was confirmed that pH of solution had a positive impact on dye removal while feed temperature showed a different image. A comparison was made between the results of dye removal in biological and membrane methods. The results showed that membrane method had higher removal potential with lower effective cost. The present study indicates that the use of NF membrane in dye removal from the effluent of Iraqi textile mills is promising.
Related collections
Most cited references13
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Remediation of dyes in textile effluent: a critical review on current treatment technologies with a proposed alternative.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Reactive dye removal in dye/salt mixtures by nanofiltration membranes containing vinylsulphone dyes: effects of feed concentration and cross flow velocity
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found