- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Effect of sutureless scleral fixed intraocular lens implantation on aphakic eyes: a system review and meta-analysis
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Sutureless scleral fixed intraocular lens implantation (SF-IOL) has become one of the mainstream schemes in clinical treatment of aphakic eyes because of its advantages, such as avoiding dislocation of intraocular lens or subluxation caused by suture degradation or fracture and significant improvement of postoperative visual acuity. However, a consensus on the relative effectiveness and safety of this operation and other methods is still lacking. This study aimed to compare the efficacy and safety of sutureless SF-IOL with other methods. Aphakia means that the lens leaves the normal position and loses its original function, including absence or complete dislocation and subluxation of the lens which could cause anisometropic amblyopia, strabismus, and loss of binocular function in children and adolescents. For adults, the loss of the lens could lead to high hyperopia and affect vision. Above all this disease can seriously affect the quality of life of patients.
Methods
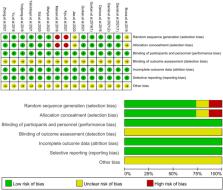
Literature about sutureless SF-IOL in PubMed, Cochrane Library, Embase, Web of Science, China National Knowledge Infrastructure, China Technical Journal VIP database, and Wanfang database published from 2000 to 2022 was reviewed. The weighted average difference was calculated by RevMan5.3 software for analysis. Two researchers independently selected the study and used the Cochrane collaboration tool to assess the risk of errors. Cochrane bias risk tool was used to evaluate the quality of evidence. This study is registered on PROSPERO (CRD42022363282).
Results
The postoperative IOL-related astigmatism of sutureless SF-IOL was lower than that of suture SF-IOL, and there was statistical difference when we compared the absolute postoperative spherical equivalent after sutureless SF-IOL and suture SF-IOL. Indicating that the degree of refractive error after sutureless SF-IOL was lower. Meanwhile, the operation time of sutureless SF-IOL was shorter than that of suture SF-IOL. The subgroup analysis showed that the absolute postoperative spherical equivalent and astigmatism values in Yamane technique were lower than those in suture SF-IOL.
Related collections
Most cited references33
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
GRADE: an emerging consensus on rating quality of evidence and strength of recommendations.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Fibrin glue-assisted sutureless posterior chamber intraocular lens implantation in eyes with deficient posterior capsules.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found