- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A feasibility study on bedside upper airway ultrasonography compared to waveform capnography for verifying endotracheal tube location after intubation
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
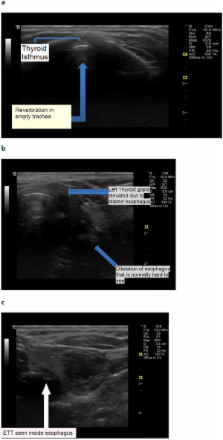
In emergency settings, verification of endotracheal tube (ETT) location is important for critically ill patients. Ignorance of oesophageal intubation can be disastrous. Many methods are used for verification of the endotracheal tube location; none are ideal. Quantitative waveform capnography is considered the standard of care for this purpose but is not always available and is expensive. Therefore, this feasibility study is conducted to compare a cheaper alternative, bedside upper airway ultrasonography to waveform capnography, for verification of endotracheal tube location after intubation.
Methods
This was a prospective, single-centre, observational study, conducted at the HRPB, Ipoh. It included patients who were intubated in the emergency department from 28 March 2012 to 17 August 2012. A waiver of consent had been obtained from the Medical Research Ethics Committee. Bedside upper airway ultrasonography was performed after intubation and compared to waveform capnography. Specificity, sensitivity, positive and negative predictive value and likelihood ratio are calculated.
Results
A sample of 107 patients were analysed, and 6 (5.6%) had oesophageal intubations. The overall accuracy of bedside upper airway ultrasonography was 98.1% (95% confidence interval (CI) 93.0% to 100.0%). The kappa value ( Κ) was 0.85, indicating a very good agreement between the bedside upper airway ultrasonography and waveform capnography. Thus, bedside upper airway ultrasonography is in concordance with waveform capnography. The sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of bedside upper airway ultrasonography were 98.0% (95% CI 93.0% to 99.8%), 100% (95% CI 54.1% to 100.0%), 100% (95% CI 96.3% to 100.0%) and 75.0% (95% CI 34.9% to 96.8%). The likelihood ratio of a positive test is infinite and the likelihood ratio of a negative test is 0.0198 (95% CI 0.005 to 0.0781). The mean confirmation time by ultrasound is 16.4 s. No adverse effects were recorded.
Related collections
Most cited references42
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Comparison of three different methods to confirm tracheal tube placement in emergency intubation.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A simple nomogram for sample size for estimating sensitivity and specificity of medical tests
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found