- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
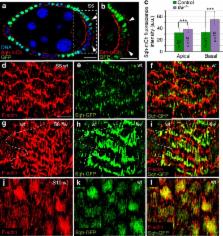
Myosin light-chain phosphatase regulates basal actomyosin oscillations during morphogenesis
Read this article at
Abstract
Contractile actomyosin networks generate forces that drive tissue morphogenesis. Actomyosin contractility is controlled primarily by reversible phosphorylation of the myosin-II regulatory light chain through the action of myosin kinases and phosphatases. While the role of myosin light-chain kinase in regulating contractility during morphogenesis has been largely characterized, there is surprisingly little information on myosin light-chain phosphatase (MLCP) function in this context. Here, we use live imaging of Drosophila follicle cells combined with mathematical modelling to demonstrate that the MLCP subunit flapwing ( flw) is a key regulator of basal myosin oscillations and cell contractions underlying egg chamber elongation. Flw expression decreases specifically on the basal side of follicle cells at the onset of contraction and flw controls the initiation and periodicity of basal actomyosin oscillations. Contrary to previous reports, basal F-actin pulsates similarly to myosin. Finally, we propose a quantitative model in which periodic basal actomyosin oscillations arise in a cell-autonomous fashion from intrinsic properties of motor assemblies.
Abstract
 Actomyosin contractility is regulated by phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light
chain; much of the work in this area has focused on the kinase. Here the authors use
Drosophila follicle cells and modelling to show that the phosphatase subunit Flapwing controls
the initiation and dynamics of actomyosin oscillations.
Actomyosin contractility is regulated by phosphorylation of myosin regulatory light
chain; much of the work in this area has focused on the kinase. Here the authors use
Drosophila follicle cells and modelling to show that the phosphatase subunit Flapwing controls
the initiation and dynamics of actomyosin oscillations.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Non-muscle myosin II takes centre stage in cell adhesion and migration.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Planar polarized actomyosin contractile flows control epithelial junction remodelling.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found