- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Comparative Study of the Use of Harmonic Scalpel versus Unipolar Cautery in Modified Radical Mastectomy
Read this article at
Abstract
Context:
Oncosurgery is an emerging branch with the set goals of prolonging the life and ensuring the best possible quality of life to the surviving patient. The use of harmonic scalpel has proved to be beneficial in a variety of surgeries but its role in breast surgery is still controversial.
Aims:
We conducted this study to compare the intraoperative and postoperative outcomes in modified radical mastectomy using harmonic scalpel versus electrocautery.
Subjects and Methods:
Fifty female patients with confirmed diagnosis of breast carcinoma and planned for modified radical mastectomy were taken up for surgery. Twenty-five patients were operated using harmonic scalpel (Group A) and another 25 were operated using unipolar cautery (Group B).
Results:
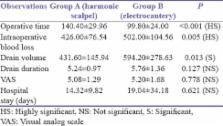
The mean operative time was significantly longer with harmonic scalpel when compared to that with electrocautery (140.40 ± 29.96 vs. 99.80 ± 24.00 min, P < 0.001). The smaller amount of drainage content (431.60 ± 145.94 vs. 594.20 ± 278.63, P = 0.013) and intraoperative blood loss (426.00 ± 76.54 vs. 502.00 ± 104.56, P = 0.005) in the group operated with the ultrasound harmonic scalpel was statistically significant. There was no significant difference between the groups with regard to drain duration (5.24 ± 0.97, P = 0.127), seroma (12% vs. 16%, P = 0.684), hematoma (4% vs. 4%, P = 1.000), wound infection (24% vs. 32%, P = 0.529), flap necrosis (8% vs. 28%, P = 0.066), pain intensity (measured on visual analog scale) (5.08 ± 1.29 vs. 5.20 ± 1.68, P = 0.778), and lymphedema (4% vs. 8%, P = 0.552). The length of hospital stay could not be compared effectively because all the patients were discharged on the 10 th or 11 th postoperative day. The cost of the equipment used in the electrocautery group was almost negligible as compared to the harmonic group.
Related collections
Most cited references26
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Impact of aging on the biology of breast cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Systemic cytokine response after major surgery.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found