- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Formulation for the Targeted Delivery of a Vaccine Strain of Oncolytic Measles Virus (OMV) in Hyaluronic Acid Coated Thiolated Chitosan as a Green Nanoformulation for the Treatment of Prostate Cancer: A Viro-Immunotherapeutic Approach

Abstract
Methodology
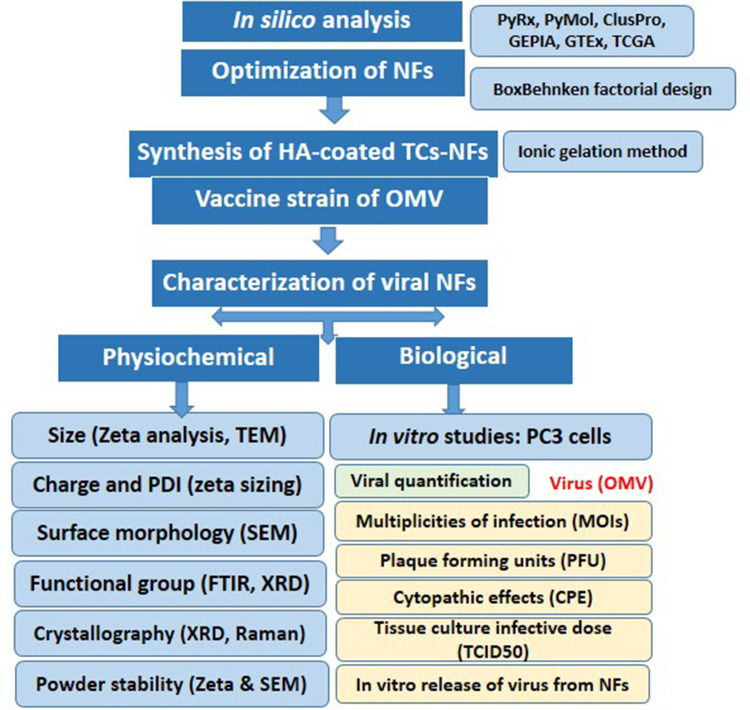
In the present work, a live attenuated oral measles vaccine (OMV) strain was used to formulate a polymeric surface-functionalized ligand-based nanoformulation (NF). OMV (half dose: not less than 500 TCID units; 0.25 mL) was encapsulated in thiolated chitosan and outermost coating with hyaluronic acid by ionic gelation method characterizing parameters was performed.
Results and Discussion
CD44 high expression was confirmed in prostatic adenocarcinoma (PRAD) by GEPIA which extracted data of normal and cancer tissue from GTEx and TCGA. Bioinformatics tools confirmed the viral hemagglutinin capsid protein interaction with human Caspase-I, NLRP3, and TNF-α and viral fusion protein interaction with COX-II and Caspase-I after successful delivery of MV encapsulated in NFs due to high affinity of hyaluronic acid with CD44 on the surface of prostate cancer cells. Particle size = 275.6 mm, PDI = 0.372, and ±11.5 zeta potential were shown by zeta analysis, while the thiolated group in NFs was confirmed by FTIR and Raman analysis. SEM and XRD showed a spherical smooth surface and crystalline nature, respectively, while TEM confirmed virus encapsulation within nanoparticles, which makes it very useful in targeted virus delivery systems. The virus was released from NFs in a sustained but continuous release pattern till 48 h. The encapsulated virus titer was calculated as 2.34×107 TCID50/mL units, which showed syncytia formation on post-day infection 7. Multiplicities of infection 0.1, 0.5, 1, 3, 5, 10, 15, and 20 of HA-coated OMV-loaded NFs as compared to MV vaccine on PC3 was inoculated with IC50 of 5.1 and 3.52, respectively, and growth inhibition was seen after 72 h via MTT assay which showed apoptotic cancer cell death.
Graphical Abstract
Most cited references40
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Caspase-1-induced pyroptosis is an innate immune effector mechanism against intracellular bacteria

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cancer nanomedicine: a review of recent success in drug delivery
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found