- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition and its transcription factors
Read this article at
Abstract
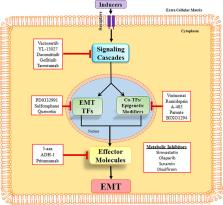
Epithelial–mesenchymal transition or EMT is an extremely dynamic process involved in conversion of epithelial cells into mesenchymal cells, stimulated by an ensemble of signaling pathways, leading to change in cellular morphology, suppression of epithelial characters and acquisition of properties such as enhanced cell motility and invasiveness, reduced cell death by apoptosis, resistance to chemotherapeutic drugs etc. Significantly, EMT has been found to play a crucial role during embryonic development, tissue fibrosis and would healing, as well as during cancer metastasis. Over the years, work from various laboratories have identified a rather large number of transcription factors (TFs) including the master regulators of EMT, with the ability to regulate the EMT process directly. In this review, we put together these EMT TFs and discussed their role in the process. We have also tried to focus on their mechanism of action, their interdependency, and the large regulatory network they form. Subsequently, it has become clear that the composition and structure of the transcriptional regulatory network behind EMT probably varies based upon various physiological and pathological contexts, or even in a cell/tissue type-dependent manner.
Related collections
Most cited references248
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Molecular mechanisms of epithelial-mesenchymal transition.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found