- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The use of the Gail model, body mass index and SNPs to predict breast cancer among women with abnormal (BI-RADS 4) mammograms
Read this article at
Abstract
Introduction
Mammography screening results in a significant number of false-positives. The use of pretest breast cancer risk factors to guide follow-up of abnormal mammograms could improve the positive predictive value of screening. We evaluated the use of the Gail model, body mass index (BMI), and genetic markers to predict cancer diagnosis among women with abnormal mammograms. We also examined the extent to which pretest risk factors could reclassify women without cancer below the biopsy threshold.
Methods
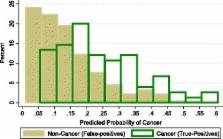
We recruited a prospective cohort of women referred for biopsy with abnormal (BI-RADS 4) mammograms according to the American College of Radiology’s Breast Imaging-Reporting and Data System (BI-RADS). Breast cancer risk factors were assessed prior to biopsy. A validated panel of 12 single-nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) associated with breast cancer were measured. Logistic regression was used to assess the association of Gail risk factors, BMI and SNPs with cancer diagnosis (invasive or ductal carcinoma in situ). Model discrimination was assessed using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve, and calibration was assessed using the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness-of-fit test. The distribution of predicted probabilities of a cancer diagnosis were compared for women with or without breast cancer.
Results
In the multivariate model, age (odds ratio (OR) = 1.05; 95% confidence interval (CI), 1.03 to 1.08; P < 0.001), SNP panel relative risk (OR = 2.30; 95% CI, 1.06 to 4.99, P = 0.035) and BMI (≥30 kg/m 2 versus <25 kg/m 2; OR = 2.20; 95% CI, 1.05 to 4.58; P = 0.036) were significantly associated with breast cancer diagnosis. Older women were more likely than younger women to be diagnosed with breast cancer. The SNP panel relative risk remained strongly associated with breast cancer diagnosis after multivariable adjustment. Higher BMI was also strongly associated with increased odds of a breast cancer diagnosis. Obese women (OR = 2.20; 95% CI, 1.05 to 4.58; P = 0.036) had more than twice the odds of cancer diagnosis compared to women with a BMI <25 kg/m 2. The SNP panel appeared to have predictive ability among both white and black women.
Related collections
Most cited references59
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A genome-wide association study identifies alleles in FGFR2 associated with risk of sporadic postmenopausal breast cancer.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Projecting individualized probabilities of developing breast cancer for white females who are being examined annually.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found