- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Troponins and Natriuretic Peptides in Cardio-Oncology Patients—Data From the ECoR Registry
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
The long-term survival of cancer patients has significantly improved over the past years. Despite their therapeutic efficacy, various cancer therapies are associated with cardiotoxicity. Therefore, timely detection of cardiotoxic adverse events is crucial. However, the clinical assessment of myocardial damage caused by cancer therapy remains difficult.
Methods
This retrospective study was performed to evaluate the diagnostic value of cardiac troponin I (cTnI) and N-terminal pro-B-type natriuretic peptide (NT-proBNP) for monitoring cancer therapy-induced cardiomyopathy. A total of 485 cancer patients referred to our cardio-oncology unit between July 2018 and January 2020 were selected from our Essen Cardio-oncology Registry (ECoR). We included patients with all types of cancer. Plasma concentrations of cTnI and NT-proBNP were measured by radioimmunoassay, and two-dimensional left ventricular ejection fraction (2D-LVEF), diastolic function, and global longitudinal strain (GLS) were measured by transthoracic echocardiography. In 116 patients, assessment was conducted before the induction of cancer therapy and during a short-term follow-up period; n = 42 of these were treated for malignant melanoma, and n = 42 with serial measurements were under treatment for breast cancer.
Results
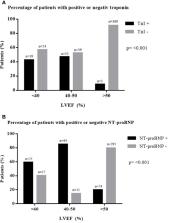
In cross-sectional data, elevated NT-proBNP was associated with reduced LVEF and pathological GLS in the total cohort. A total of 116 patients had serial LVEF and biomarker measurements, and changes in NT-proBNP and troponin correlated with changes in LVEF during follow-up investigations. Similar to the total cohort, a subgroup of patients treated for malignant melanoma showed a correlation between the change in cTnI and the change in LVEF. In a subgroup analysis of patients undergoing breast cancer therapy, a correlation between the change in NT-proBNP and the change in LVEF could be detected. Thirty patients presented with chemotherapy-induced cardiomyopathy, defined as a significant LVEF decrease (> 10%) to a value below 50%. The number of patients with increased cTnI and NT-proBNP was significantly higher in patients with chemotherapy-induced cardiomyopathy than in patients without cardiotoxicity. Patients with positive cTnI and NT-proBNP were more likely to have a history of coronary heart disease, atrial fibrillation, and arterial hypertension.
Related collections
Most cited references43
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Guidelines for Performing a Comprehensive Transthoracic Echocardiographic Examination in Adults: Recommendations from the American Society of Echocardiography
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found