- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Asphaltene Remediation and Improved Oil Recovery by Advanced Solvent Deasphalting Technology
Read this article at
Abstract

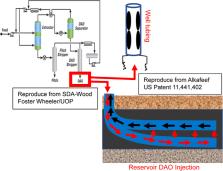
Resin molecules play a crucial role in the stability of colloidal asphaltene particles in petroleum reservoirs. De-stabilization of the asphaltene/resin interaction due to changes in thermodynamic parameters can cause asphaltene precipitation, thus leading to petroleum field problems such as decreased in situ permeability, as well as severe plugging problems in production facilities. One remedial technology used in the oil industry involves developing synthetic resins with enhanced chemical potential to increase the stability of asphaltene in the oil phase. However, accurately predicting what synthetic resin structures are compatible with asphaltenes in this context can be difficult and ineffective. Here, we introduce a method that enhances the stability of colloidal asphaltene in petroleum fluid by increasing the concentrations of natural-state oil resins and increases reservoir oil recovery by increasing the oil’s aromatic power solvency. The stability of colloidal asphaltene and improvements in oil reservoir recovery were investigated by using an oil prefractionation process and a solvent deasphalting technology based on the residuum oil supercritical extraction process to develop three types of deasphalted oils derived from Kuwait Marrat oil. Using these methods, we found that resin concentration by volume in Marrat oil increased with the removal of more oil fractions. Asphaltene stability in the oil phase was strongly influenced by resin concentration. The deasphalted oils’ aromatic power solvency increased the oil reservoir permeability by twofold. No formation damage was observed for all DAO products in core flooding tests.
Related collections
Most cited references32
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Asphaltic Bitumen as Colloid System.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Influence of Temperature and Pressure on Asphaltene Flocculation
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found