- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Neurodegenerative Diseases – Is Metabolic Deficiency the Root Cause?
Read this article at
Abstract
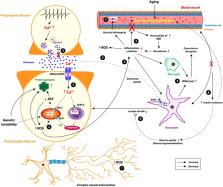
Neurodegenerative diseases, including Alzheimer, Parkinson, Huntington, and amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, are a prominent class of neurological diseases currently without a cure. They are characterized by an inexorable loss of a specific type of neurons. The selective vulnerability of specific neuronal clusters (typically a subcortical cluster) in the early stages, followed by the spread of the disease to higher cortical areas, is a typical pattern of disease progression. Neurodegenerative diseases share a range of molecular and cellular pathologies, including protein aggregation, mitochondrial dysfunction, glutamate toxicity, calcium load, proteolytic stress, oxidative stress, neuroinflammation, and aging, which contribute to neuronal death. Efforts to treat these diseases are often limited by the fact that they tend to address any one of the above pathological changes while ignoring others. Lack of clarity regarding a possible root cause that underlies all the above pathologies poses a significant challenge. In search of an integrative theory for neurodegenerative pathology, we hypothesize that metabolic deficiency in certain vulnerable neuronal clusters is the common underlying thread that links many dimensions of the disease. The current review aims to present an outline of such an integrative theory. We present a new perspective of neurodegenerative diseases as metabolic disorders at molecular, cellular, and systems levels. This helps to understand a common underlying mechanism of the many facets of the disease and may lead to more promising disease-modifying therapeutic interventions. Here, we briefly discuss the selective metabolic vulnerability of specific neuronal clusters and also the involvement of glia and vascular dysfunctions. Any failure in satisfaction of the metabolic demand by the neurons triggers a chain of events that precipitate various manifestations of neurodegenerative pathology.
Related collections
Most cited references185
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Stages in the development of Parkinson's disease-related pathology.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found