- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Elucidation of Shearing Mechanism of Finish-type FB and Extrusion-type FB for Thin Foil of JIS SUS304 by Numerical and EBSD Analyses
Read this article at
Abstract
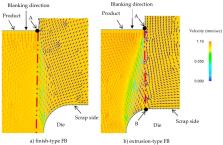
A numerical analysis using FE (finite element) analysis was performed to clarify the shearing mechanism in the process of extrusion-type fine blanking (FB) for a thin foil of JIS SUS304 in this study. Extrusion-type FB, in which a negative clearance between the punch and the die has been developed and investigated experimentally to improve the quality of the sheared surface in the blanking of thin foils. The resultant sheared surface for extrusion-type FB indicated an almost completely sheared surface, and the fracture portion on the sheared surface was much smaller than that in conventional FB, the so-called finish-type FB. The material flow and fracture criteria in extrusion-type FB were analyzed in comparison with those in finish-type FB. The differences in material flow and so-called critical fracture value were verified for the two processes. The principal stress near the shearing surface has mostly compressive components in extrusion-type FB due to its negative clearance, and the critical fracture value was also less than that in finish-type FB, in which the principal stress near the shearing surface has mostly tensile components. Furthermore, SEM observation with EBSD (electron back-scatter diffraction) analysis of the shearing surface was performed to verify the phenomena. Reductions in deformation-induced crystal orientation rotation and martensite transformation in extrusion-type FB were confirmed in comparison with those in finish-type FB from the analysis results.
Related collections
Most cited references19
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Influence of specimen dimensions on the tensile behavior of ultrafine-grained Cu
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Influence of specimen dimensions and strain measurement methods on tensile stress–strain curves
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found