- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Solid Fat Replacement with Canola Oil-Carnauba Wax Oleogels for Dairy-Free Imitation Cheese Low in Saturated Fat
Read this article at
Abstract
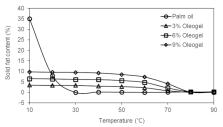
Canola oil was structured into oleogels with different amounts of carnauba wax, and their processing performances were assessed as an alternative to solid fat for imitation cheese low in saturated fat. The contents of solid fat in the oleogels were less vulnerable to the change in temperature than the palm oil. The replacement of palm oil with oleogels produced cheese samples with harder and more cohesive/chewy textures. Dynamic and transient viscoelastic measurements demonstrated that the use of oleogels was effective in increasing the elastic nature of the cheeses. Two distinct components with different proton mobilities were observed in the imitation cheeses, and longer T 2 relaxation times were detected in the oleogel samples. The meltability of the cheese with palm oil was not significantly different from those with 3% and 6% oleogels. The saturated fat level of the oleogel cheese was significantly reduced from 45.70 to 5.20%. The application of canola oil-carnauba wax oleogels could successfully produce imitation cheese high in unsaturated fat and low in saturated fat. This study thus demonstrated that the health-functional properties of imitation cheese could be enhanced by using oleogels.
Related collections
Most cited references52
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
WHO draft guidelines on dietary saturated and trans fatty acids: time for a new approach?
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Oleogels, a promising structured oil for decreasing saturated fatty acid concentrations: Production and food-based applications
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found