- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
LSTM-driven drug design using SELFIES for target-focused de novo generation of HIV-1 protease inhibitor candidates for AIDS treatment
Read this article at
Abstract
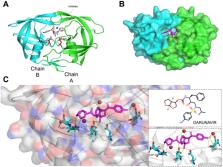
The battle against viral drug resistance highlights the need for innovative approaches to replace time-consuming and costly traditional methods. Deep generative models offer automation potential, especially in the fight against Human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), as they can synthesize diverse molecules effectively. In this paper, an application of an LSTM-based deep generative model named “LSTM-ProGen” is proposed to be tailored explicitly for the de novo design of drug candidate molecules that interact with a specific target protein (HIV-1 protease). LSTM-ProGen distinguishes itself by employing a long-short-term memory (LSTM) architecture, to generate novel molecules target specificity against the HIV-1 protease. Following a thorough training process involves fine-tuning LSTM-ProGen on a diverse range of compounds sourced from the ChEMBL database. The model was optimized to meet specific requirements, with multiple iterations to enhance its predictive capabilities and ensure it generates molecules that exhibit favorable target interactions. The training process encompasses an array of performance evaluation metrics, such as drug-likeness properties. Our evaluation includes extensive silico analysis using molecular docking and PCA-based visualization to explore the chemical space that the new molecules cover compared to those in the training set. These evaluations reveal that a subset of 12 de novo molecules generated by LSTM-ProGen exhibit a striking ability to interact with the target protein, rivaling or even surpassing the efficacy of native ligands. Extended versions with further refinement of LSTM-ProGen hold promise as versatile tools for designing efficacious and customized drug candidates tailored to specific targets, thus accelerating drug development and facilitating the discovery of new therapies for various diseases.
Related collections
Most cited references29
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
DrugBank 5.0: a major update to the DrugBank database for 2018

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Open Babel: An open chemical toolbox
Author and article information
Contributors
Journal
Affiliations
Author notes
Author information
Article
Publisher ID: PONE-D-24-04274This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.