- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Agricultural pesticide use and adverse birth outcomes in the San Joaquin Valley of California
Read this article at
Abstract
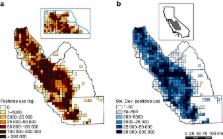
Virtually all agricultural communities worldwide are exposed to agricultural pesticides. Yet, the health consequences of such exposure are poorly understood, and the scientific literature remains ambiguous. Using individual birth and demographic characteristics for over 500 000 birth observations between 1997–2011 in the agriculturally dominated San Joaquin Valley, California, we statistically investigate if residential agricultural pesticide exposure during gestation, by trimester, and by toxicity influences birth weight, gestational length, or birth abnormalities. Overall, our analysis indicates that agricultural pesticide exposure increases adverse birth outcomes by 5–9%, but only among the population exposed to very high quantities of pesticides (e.g., top 5th percentile, i.e., ~4200 kg applied over gestation). Thus, policies and interventions targeting the extreme right tail of the pesticide distribution near human habitation could largely eliminate the adverse birth outcomes associated with agricultural pesticide exposure documented in this study.
Abstract
The health consequences of exposure to pesticides are uncertain and subject to much debate. Here, the effect of exposure during pregnancy is investigated in an agriculturally dominated residential area, showing that an increase in adverse birth outcomes is observed with very high levels of pesticide exposure.
Related collections
Most cited references37
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Assessing the impact of the green revolution, 1960 to 2000.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Association of in Utero Organophosphate Pesticide Exposure and Fetal Growth and Length of Gestation in an Agricultural Population
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found