- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Inhibition of TRPV1 by SHP-1 in nociceptive primary sensory neurons is critical in PD-L1 analgesia

Read this article at
Abstract
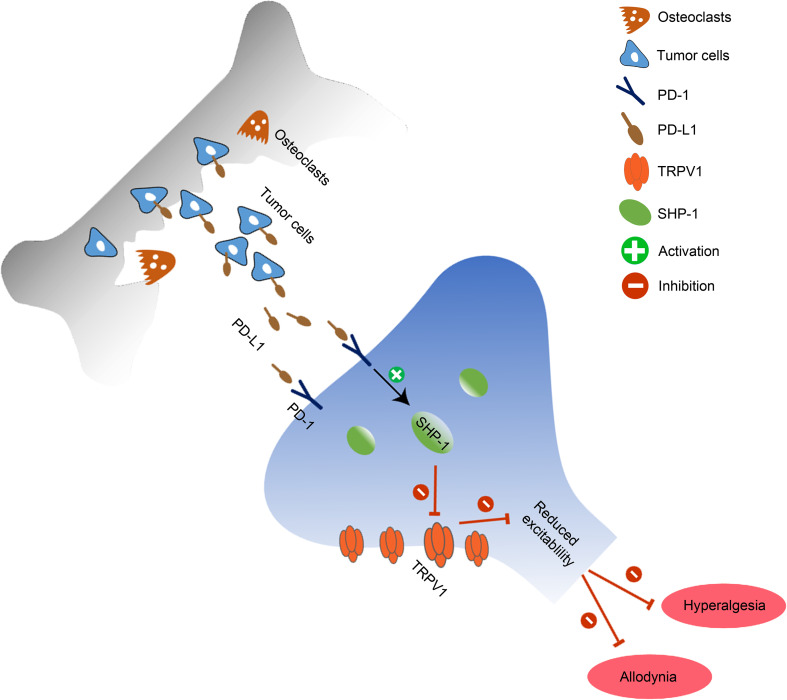
Recently programmed death-ligand 1 (PD-L1) receptor PD-1 was found in dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons, and PD-L1 activates PD-1 to inhibit inflammatory and neuropathic pain by modulating neuronal excitability. However, the downstream signaling of PD-1 in sensory neurons remains unclear. Here, we show that PD-L1 activated Src homology 2 domain-containing tyrosine phosphatase-1 (SHP-1) to downregulate transient receptor potential vanilloid 1 (TRPV1) in DRG neurons and inhibit bone cancer pain in mice. Local injection of PD-L1 produced analgesia. PD-1 in DRG neurons colocalized with TRPV1 and SHP-1. PD-L1 induced the phosphorylation of SHP-1 in DRG TRPV1 neurons and inhibited TRPV1 currents. Loss of TRPV1 in mice abolished bone cancer–induced thermal hyperalgesia and PD-L1 analgesia. Conditioned deletion of SHP-1 in Na V1.8 + neurons aggravated bone cancer pain and diminished the inhibition of PD-L1 on TRPV1 currents and pain. Together, our findings suggest that PD-L1/PD-1 signaling suppresses bone cancer pain via inhibition of TRPV1 activity. Our results also suggest that SHP-1 in sensory neurons is an endogenous pain inhibitor and delays the development of bone cancer pain via suppressing TRPV1 function.
Abstract
Abstract
PD-L1/PD-1 signaling suppresses TRPV1 activity and alleviates pain-like behaviors via phosphorylation of SHP-1 in nociceptive primary sensory neurons in a mouse bone cancer model.
Related collections
Most cited references79
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Safety and Activity of Anti–PD-L1 Antibody in Patients with Advanced Cancer
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
PD-1 and its ligands in tolerance and immunity.

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found