- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Localization of seismic waves with submarine fiber optics using polarization-only measurements
Read this article at
Abstract
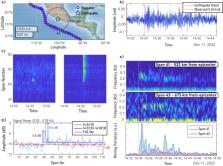
Monitoring seismic activity on the ocean floor is a critical yet challenging task, largely due to the difficulties of physical deployment and maintenance of sensors in these remote areas. Optical fiber sensing techniques are well-suited for this task, given the presence of existing transoceanic telecommunication cables. However, current techniques capable of interrogating the entire length of transoceanic fibers are either incompatible with conventional telecommunication lasers or are limited in their ability to identify the position of the seismic wave. In this work, we propose and demonstrate a method to measure and localize seismic waves in transoceanic cables using only conventional polarization optics, by launching pulses of changing polarization. We demonstrate our technique by measuring and localizing seismic waves from a magnitude M w 6.0 earthquake (Guerrero, Mexico) using a submarine cable connecting Los Angeles, California and Valparaiso, Chile. Our approach introduces a cost-effective and practical solution that can potentially increase the density of geophysical measurements in hard-to-reach regions, improving disaster preparedness and response, with minimal additional demands on existing infrastructure.
Abstract
Costa and co-authors detected an earthquake in Mexico using conventional polarisation optics within a trans-oceanic fibre-optic cable connecting Los Angeles, USA with Valparaiso, Chile. Their approach enables non-invasive monitoring and localization of seismic waves on the seabed.
Related collections
Most cited references15
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Ultrastable laser interferometry for earthquake detection with terrestrial and submarine cables
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found