- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Drug-induced oxidative stress in cancer treatments: Angel or devil?
Read this article at
Abstract
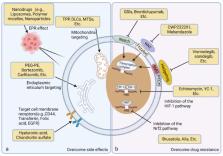
Oxidative stress (OS), defined as redox imbalance in favor of oxidant burden, is one of the most significant biological events in cancer progression. Cancer cells generally represent a higher oxidant level, which suggests a dual therapeutic strategy by regulating redox status (i.e., pro-oxidant therapy and/or antioxidant therapy). Indeed, pro-oxidant therapy exhibits a great anti-cancer capability, attributing to a higher oxidant accumulation within cancer cells, whereas antioxidant therapy to restore redox homeostasis has been claimed to fail in several clinical practices. Targeting the redox vulnerability of cancer cells by pro-oxidants capable of generating excessive reactive oxygen species (ROS) has surfaced as an important anti-cancer strategy. However, multiple adverse effects caused by the indiscriminate attacks of uncontrolled drug-induced OS on normal tissues and the drug-tolerant capacity of some certain cancer cells greatly limit their further applications. Herein, we review several representative oxidative anti-cancer drugs and summarize their side effects on normal tissues and organs, emphasizing that seeking a balance between pro-oxidant therapy and oxidative damage is of great value in exploiting next-generation OS-based anti-cancer chemotherapeutics.
Related collections
Most cited references256
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Reactive oxygen species (ROS) as pleiotropic physiological signalling agents
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
A new concept for macromolecular therapeutics in cancer chemotherapy: mechanism of tumoritropic accumulation of proteins and the antitumor agent smancs.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found