- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Persistent neurologic symptoms and cognitive dysfunction in non‐hospitalized Covid‐19 “long haulers”
Abstract
Objective
Most SARS‐CoV‐2‐infected individuals never require hospitalization. However, some develop prolonged symptoms. We sought to characterize the spectrum of neurologic manifestations in non‐hospitalized Covid‐19 “long haulers”.
Methods
This is a prospective study of the first 100 consecutive patients (50 SARS‐CoV‐2 laboratory‐positive (SARS‐CoV‐2 +) and 50 laboratory‐negative (SARS‐CoV‐2 ‐) individuals) presenting to our Neuro‐Covid‐19 clinic between May and November 2020. Due to early pandemic testing limitations, patients were included if they met Infectious Diseases Society of America symptoms of Covid‐19, were never hospitalized for pneumonia or hypoxemia, and had neurologic symptoms lasting over 6 weeks. We recorded the frequency of neurologic symptoms and analyzed patient‐reported quality of life measures and standardized cognitive assessments.
Results
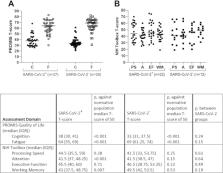
Mean age was 43.2 ± 11.3 years, 70% were female, and 48% were evaluated in televisits. The most frequent comorbidities were depression/anxiety (42%) and autoimmune disease (16%). The main neurologic manifestations were: “brain fog” (81%), headache (68%), numbness/tingling (60%), dysgeusia (59%), anosmia (55%), and myalgias (55%), with only anosmia being more frequent in SARS‐CoV‐2 + than SARS‐CoV‐2 ‐ patients (37/50 [74%] vs. 18/50 [36%]; p < 0.001). Moreover, 85% also experienced fatigue. There was no correlation between time from disease onset and subjective impression of recovery. Both groups exhibited impaired quality of life in cognitive and fatigue domains. SARS‐CoV‐2 + patients performed worse in attention and working memory cognitive tasks compared to a demographic‐matched US population (T‐score 41.5 [37, 48.25] and 43 [37.5, 48.75], respectively; both p < 0.01).
Related collections
Most cited references69
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Clinical Characteristics of Coronavirus Disease 2019 in China
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found