- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Cytokine Tuning of Intestinal Epithelial Function
Read this article at
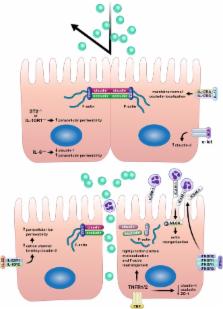
Abstract
The intestine serves as both our largest single barrier to the external environment and the host of more immune cells than any other location in our bodies. Separating these potential combatants is a single layer of dynamic epithelium composed of heterogeneous epithelial subtypes, each uniquely adapted to carry out a subset of the intestine’s diverse functions. In addition to its obvious role in digestion, the intestinal epithelium is responsible for a wide array of critical tasks, including maintaining barrier integrity, preventing invasion by microbial commensals and pathogens, and modulating the intestinal immune system. Communication between these epithelial cells and resident immune cells is crucial for maintaining homeostasis and coordinating appropriate responses to disease and can occur through cell-to-cell contact or by the release or recognition of soluble mediators. The objective of this review is to highlight recent literature illuminating how cytokines and chemokines, both those made by and acting on the intestinal epithelium, orchestrate many of the diverse functions of the intestinal epithelium and its interactions with immune cells in health and disease. Areas of focus include cytokine control of intestinal epithelial proliferation, cell death, and barrier permeability. In addition, the modulation of epithelial-derived cytokines and chemokines by factors such as interactions with stromal and immune cells, pathogen and commensal exposure, and diet will be discussed.
Related collections
Most cited references108
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Intestinal epithelial cells: regulators of barrier function and immune homeostasis.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Regional specialization within the intestinal immune system.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found