- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Sentinel lymph node biopsy in T1/T2 squamous cell carcinomas of the tongue: A prospective study
Read this article at
Abstract
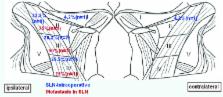
Commonly used staging procedures often cannot predict the absence of cervical metastases (CM) in squamous cell carcinomas (SCCs) of the oral cavity. Due to the high incidence of occult CM in numerous N0 cases in the clinic, an elective neck dissection (ND) is performed. The sentinel lymph node biopsy (SNB) is a common concept in the modern surgical therapy of malignancies. The present study evaluates the applicability of this concept for T1/T2-SCC of the tongue. In a prospective clinical study, 10 consecutive patients with T1/T2-SCC of the tongue and cN0 necks, were enrolled. Following sentinel lymph node (SLN) scintigraphy, all patients underwent SNB with a γ-probe and a subsequent ND. SNB specimens were compared with histopathological assessments of surgical specimens from the ND. A total of 5 female and 5 male patients (mean age, 52 years; women, 62 years; men, 42 years), with a median follow-up time of 33.5 months (range, 10–40 months), were treated. All patients presented with detectable SLNs. In 7 cases, the SLN(s) and the residual ND were negative for CM. In 3 cases, the SLN(s) were positive without further CM in the other neck nodes. Furthermore, 1 patient showed additional CMs after 10 months in the contralateral neck and lung metastasis after 18 months, but none at the time of the initial treatment. The concept of an SNB appears to be applicable to the management of the cN0 neck in small SCC of the tongue. The role of SNB in the management of SCC requires further investigation by prospective trials with larger patient numbers.
Related collections
Most cited references41
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found