- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Estrogens protect male mice from obesity complications and influence glucocorticoid metabolism
Read this article at
Abstract
Background:
Although the prevalence of obesity is higher among women than men, they are somewhat protected from the associated cardiometabolic consequences. The increase in cardiovascular disease risk seen after the menopause suggests a role for estrogens. There is also growing evidence for the importance of estrogen on body fat and metabolism in males. We hypothesized that that estrogen administration would ameliorate the adverse effects of obesity on metabolic parameters in males.
Methods:
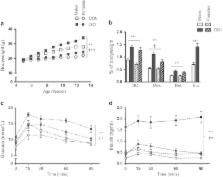
Male and female C57Bl/6 mice were fed control or obesogenic (DIO) diets from 5 weeks of age until adulthood. Glucose tolerance testing was performed at 13 weeks of age. Mice were killed at 15 weeks of age and liver and adipose tissue were collected for analysis of gene expression. A second cohort of male mice underwent the same experimental design with the addition of estradiol pellet implantation or sham surgery at 6 weeks.
Results:
DIO males had greater mesenteric adipose deposition and more severe increases in plasma glucose, insulin and lipids than females. Treatment of males with estradiol from 6 weeks of age prevented DIO-induced increases in adipose tissue mass and alterations in glucose–insulin homeostasis. We also identified sex differences in the transcript levels and activity of hepatic and adipose glucocorticoid metabolizing enzymes. Estrogen treatment feminized the pattern of DIO-induced changes in glucocorticoid metabolism, rendering males similar to females.
Conclusions:
Thus, DIO induces sex-specific changes in glucose–insulin homeostasis, which are ameliorated in males treated with estrogen, highlighting the importance of sex steroids in metabolism. Given that altered peripheral glucocorticoid metabolism has been observed in rodent and human obesity, our results also suggest that sexually dimorphic expression and activity of glucocorticoid metabolizing enzymes may have a role in the differential metabolic responses to obesity in males and females.
Related collections
Most cited references39
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
The emergence of the metabolic syndrome with menopause.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Glucocorticoids and cardiovascular disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found