- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Synthesis, analysis of molecular and crystal structures, estimation of intermolecular interactions and biological properties of 1-benzyl-6-fluoro-3-[5-(4-methylcyclohexyl)-1,2,4-oxadiazol-3-yl]-7-(piperidin-1-yl)quinolin-4-one

Read this article at
Abstract
The synthesis of the potential antimicrobial and antiviral drug, 5-[1-benzyl-6-fluoro-7-(piperidin-1-yl)-quinolin-4(1 H)-on-3-yl]-3-(4-methylcyclohex-1-yl)-1,2,4-oxadiazole, was proposed. Its molecular and crystal structures were defined and described, whereas the biological activity was predicted with molecular docking.
Abstract
The title compound, C
30H
33N
4O
2F, can be obtained
via a two-step synthetic scheme involving 1-benzyl-6-fluoro-4-oxo-7-(piperidin-1-yl)-1,4-dihydroquinoline-3-carbonitrile
as a starting compound that undergoes substitution with hydroxylamine and subsequent
cyclization with 4-methylcyclohexane-1-carboxylic acid. It crystallizes from 2-propanol
in the triclinic space group
P
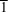 with a molecule of the title compound and one of 2-propanol in the asymmetric unit.
After the molecular structure was clarified using NMR and LC/MS, the molecular and
crystalline arrangements were defined with SC-XRD. A Hirshfeld surface analysis was
performed for a better understanding of the intermolecular interactions. One strong
(O—H⋯O) and three weak [C—H⋯F (intramolecular) and two C—H⋯O] hydrogen bonds were
found. The contributions of short contacts to the Hirshfeld surface were estimated
using two-dimensional fingerprint plots showing that O⋯H/H⋯O, C⋯H/H⋯C and C⋯C contacts
are the most significant for the title compound and O⋯H for the 2-propanol. The crystal
structure appears to have isotropically packed tetramers containing two molecules
of the title compound and two molecules of 2-propanol as the building unit according
to analysis of the distribution of pairwise interaction energies. A molecular docking
study was carried out to evaluate the interactions of the title compound with the
active centers of macromolecules corresponding to viral targets, namely, anti-hepatitis
B activity [HBV, capsid Y132A mutant (VCID 8772) PDB ID: 5E0I] and anti-COVID-19 main
protease activity (PDB ID: 6LU7). The data obtained revealed a noticeable affinity
towards them that exceeded that of the reference ligands.
with a molecule of the title compound and one of 2-propanol in the asymmetric unit.
After the molecular structure was clarified using NMR and LC/MS, the molecular and
crystalline arrangements were defined with SC-XRD. A Hirshfeld surface analysis was
performed for a better understanding of the intermolecular interactions. One strong
(O—H⋯O) and three weak [C—H⋯F (intramolecular) and two C—H⋯O] hydrogen bonds were
found. The contributions of short contacts to the Hirshfeld surface were estimated
using two-dimensional fingerprint plots showing that O⋯H/H⋯O, C⋯H/H⋯C and C⋯C contacts
are the most significant for the title compound and O⋯H for the 2-propanol. The crystal
structure appears to have isotropically packed tetramers containing two molecules
of the title compound and two molecules of 2-propanol as the building unit according
to analysis of the distribution of pairwise interaction energies. A molecular docking
study was carried out to evaluate the interactions of the title compound with the
active centers of macromolecules corresponding to viral targets, namely, anti-hepatitis
B activity [HBV, capsid Y132A mutant (VCID 8772) PDB ID: 5E0I] and anti-COVID-19 main
protease activity (PDB ID: 6LU7). The data obtained revealed a noticeable affinity
towards them that exceeded that of the reference ligands.