- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Low levels of PCSK9 are associated with remission in patients with rheumatoid arthritis treated with anti-TNF-α: potential underlying mechanisms
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
Proprotein convertase subtilisin kexin 9 (PCSK9) targets the LDL-receptor (LDLR) which raises LDL-levels. In addition, PCSK9 has proinflammatory immunological effects. Here, we investigate the role of PCSK9 in relation to the inflammatory activity in patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
PCSK9-levels were determined at baseline by ELISA in 160 patients with RA not previously treated with biologics. The patients started anti-TNF-α (adalimumab, infliximab, or etanercept) treatment and were followed-up for 1 year. Disease activity was determined by DAS28.
Effects of PCSK9 on cytokine production from macrophages of healthy individuals and synoviocytes from RA patients and inhibition by anti-PCSK9 antibodies were studied in supernatants by ELISA.
Results
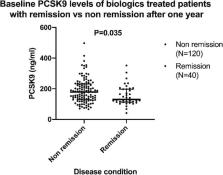
A significantly lower level of PCSK9 at baseline, p = 0.035, was observed in patients who reached remission within 1 year, defined as DAS28 < 2.6, compared to those not in remission. At 12 months of TNF-α antagonist treatment, the mean DAS28 was reduced but was significantly greater in patients with highest quartile PCSK9 (Q4) compared to those at lowest PCSK9 (Q1) in both crude ( p = 0.01) and adjusted analysis ( p = 0.004).
In vitro, PCSK9 induced TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in macrophages and monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP1) in synoviocytes. These effects were inhibited by anti-PCSK9 antibodies.
Conclusions
Low levels of PCSK9 at baseline are associated with being DAS28-responder to anti-TNF-α treatment in RA. An underlying cause could be that PCSK9 stimulates the production of proinflammatory cytokines from macrophages and synoviocytes, effects inhibited by anti-PCSK9 antibodies. PCSK9 could thus play an immunological role in RA.
Related collections
Most cited references22
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Sequence variations in PCSK9, low LDL, and protection against coronary heart disease.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Mutations in PCSK9 cause autosomal dominant hypercholesterolemia.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found