- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Electroacupuncture at Zusanli (ST36) Prevents Intestinal Barrier and Remote Organ Dysfunction following Gut Ischemia through Activating the Cholinergic Anti-Inflammatory-Dependent Mechanism
Read this article at
Abstract
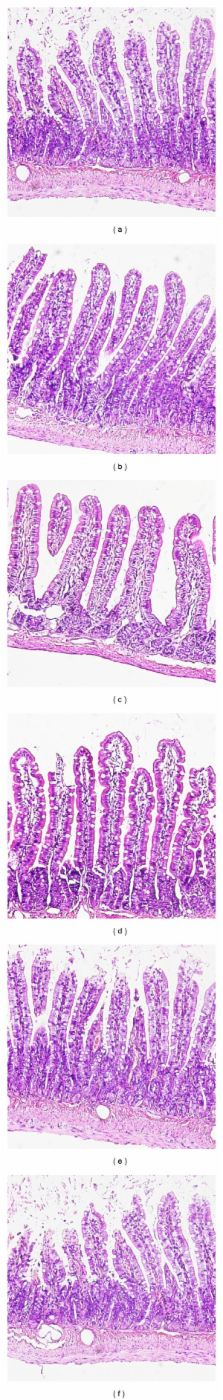
This study investigated the protective effect and mechanism of electroacupuncture at ST36 points on the intestinal barrier dysfunction and remote organ injury after intestinal ischemia and reperfusion injury in rats. Rats were subjected to gut ischemia for 30 min, and then received electroacupuncture for 30 min with or without abdominal vagotomy or intraperitoneal administration of cholinergic α 7 nicotinic acetylcholine receptor ( α 7nAChR) inhibitor. Then we compared its effects with electroacupuncture at nonchannel points, vagal nerve stimulation, or intraperitoneal administration of cholinergic agonist. Cytokine levels in plasma and tissue of intestine, lung, and liver were assessed 60 min after reperfusion. Intestinal barrier injury was detected by histology, gut injury score, the permeability to 4 kDa FITC-dextran, and changes in tight junction protein ZO-1 using immunofluorescence and Western blot. Electroacupuncture significantly lowered the levels of tumor necrosis factor- α and interleukin-8 in plasma and organ tissues, decreased intestinal permeability to FITC-dextran, and prevented changes in ZO-1 protein expression and localization. However, abdominal vagotomy or intraperitoneal administration of cholinergic α 7nAChR inhibitor reversed these effects of electroacupuncture. These findings suggest that electroacupuncture attenuates the systemic inflammatory response through protection of intestinal barrier integrity after intestinal ischemia injury in the presence of an intact vagus nerve.
Related collections
Most cited references57
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Gastrointestinal motility disorders and acupuncture.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Review article: therapeutic roles of acupuncture in functional gastrointestinal disorders.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found