- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prognostic factors in breast phyllodes tumors: a nomogram based on a retrospective cohort study of 404 patients
Read this article at
Abstract
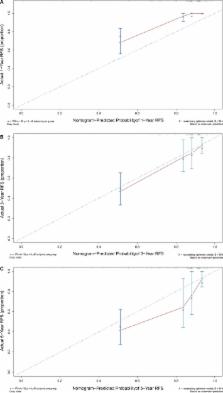
The aim of this study was to explore the independent prognostic factors related to postoperative recurrence‐free survival ( RFS) in patients with breast phyllodes tumors ( PTBs). A retrospective analysis was conducted in Fudan University Shanghai Cancer Center. According to histological type, patients with benign PTBs were classified as a low‐risk group, while borderline and malignant PTBs were classified as a high‐risk group. The Cox regression model was adopted to identify factors affecting postoperative RFS in the two groups, and a nomogram was generated to predict recurrence‐free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years. Among the 404 patients, 168 (41.6%) patients had benign PTB, 184 (45.5%) had borderline PTB, and 52 (12.9%) had malignant PTB. Fifty‐five patients experienced postoperative local recurrence, including six benign cases, 26 borderline cases, and 22 malignant cases; the three histological types of PTB had local recurrence rates of 3.6%, 14.1%, and 42.3%, respectively. Stromal cell atypia was an independent prognostic factor for RFS in the low‐risk group, while the surgical approach and tumor border were independent prognostic factors for RFS in the high‐risk group, and patients receiving simple excision with an infiltrative tumor border had a higher recurrence rate. A nomogram developed based on clinicopathologic features and surgical approaches could predict recurrence‐free survival at 1, 3, and 5 years. For high‐risk patients, this predictive nomogram based on tumor border, tumor residue, mitotic activity, degree of stromal cell hyperplasia, and atypia can be applied for patient counseling and clinical management. The efficacy of adjuvant radiotherapy remains uncertain.
Related collections
Most cited references31
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Primary treatment of cystosarcoma phyllodes of the breast.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Phyllodes tumor of the breast.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found