- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Adoption of Electronic Medical Records for Chronic Disease Care in Kenyan Refugee Camps: Quantitative and Qualitative Prospective Evaluation
Abstract
Background
Noncommunicable disease (NCD) prevention and control in humanitarian emergencies is a well-recognized need, but there is little evidence to guide responses, leading to varying care delivery. The Sana.NCD mobile health (mHealth) app, initially developed in Lebanon, is the only known mHealth tool for NCD management designed to increase care quality and coverage for providers in humanitarian settings.
Objective
We evaluated a specialized mHealth app consisting of an abbreviated medical record for patients with hypertension or diabetes, adapted for a Kenyan refugee camp setting.
Methods
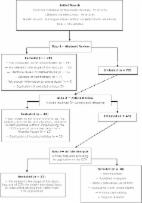
We tested an adapted version of the Sana.NCD app (diabetes and hypertension medical record) in an 11-month (May 2021 to March 2022) quantitative and qualitative prospective evaluation in Kenya’s Hagadera refugee camp. Leveraging the rollout of a general electronic medical record (EMR) system in the Kakuma refugee camp, we compared a specialized NCD management app to a general EMR. We analyzed secondary data collected from the Sana.NCD app for 1539 patients, EMR data for 68 patients with NCD from Kakuma’s surgical and outpatient departments, and key informant interviews that focused on Hagadera clinic staff perceptions of the Sana.NCD app.
Results
The Hagadera NCD clinic reported 18,801 consultations, 42.1% (n=7918) of which were reported in the NCD app. The Kakuma EMR reported 350,776 visits, of which 9385 (2.7%) were for NCDs (n=4264, 1.2% hypertension; n=2415, 0.7% diabetes). The completeness of reporting was used as a quality-of-care metric. Age, sex, prescribed medicines, random blood sugar, and smoking status were consistently reported in both the NCD app (>98%) and EMR (100%), whereas comorbidities, complications, hemoglobin A 1c, and diet were rarely reported in either platform (≤7% NCD app; 0% EMR). The number of visits, BMI, physical activity, and next visit were frequently reported in the NCD app (≥99%) but not in the EMR (≤15%). In the NCD app, the completeness of reporting was high across the implementation period, with little meaningful change. Although not significantly changed during the study, elevated blood sugar ( P=.82) and blood pressure ( P=.12) were reported for sizable proportions of patients in the first (302/481, 62.8%, and 599/1094, 54.8%, respectively) and last (374/602, 62.1%, and 720/1395, 51.6%, respectively) study quarters. Providers were satisfied with the app, as it standardized patient information and made consultations easier. Providers also indicated that access to historic patient information was easier, benefiting NCD control and follow-up.
Conclusions
A specialized record for NCDs outperformed a more general record intended for use in all patients in terms of reporting completeness. This CommCare-based NCD app can easily be rolled out in similar humanitarian settings with minimal adaptation. However, the adaptation of technologies to the local context and use case is critical for uptake and ensuring that workflows and time burden do not outweigh the benefits of EMRs.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Improving Chronic Illness Care: Translating Evidence Into Action

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Barriers to the acceptance of electronic medical records by physicians from systematic review to taxonomy and interventions
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found