- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Ventriculostomy-related infections in subarachnoid hemorrhage patients—a retrospective study of incidence, etiology, and antimicrobial therapy
Read this article at
Abstract
Background
This study was performed to investigate the incidence and etiology of ventriculostomy-related infections (VRIs) in patients with subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) and to assess adherence to local clinical guidelines regarding empirical antimicrobial therapy and diagnostic routines.
Methods
A total of 191 consecutive SAH patients treated in the neuro-intensive care unit of Uppsala University Hospital between 2010 and 2013 were included retrospectively. Information regarding cerebrospinal fluid samples, bacterial cultures, ventriculostomy treatment, patient characteristics, and antibiotic treatment were collected from electronic patient records.
Results
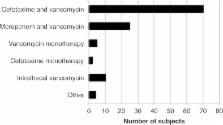
Eleven patients developed VRI, resulting in an incidence of 5.8% per patient, 5.4% per ventriculostomy catheter, and 4.1 per 1000 catheter days. Coagulase-negative staphylococci caused nine cases of VRI and Klebsiella pneumoniae and Staphylococcus aureus caused one each. Empirical VRI therapy was initiated on 97 occasions in 81 subjects (42.4%). Out of the 11 patients with VRI, four did not receive empirical antibiotic therapy before the positive culture result. The clinical actions performed after analysis of CSF samples were in line with the action suggested by the local guidelines in 307 out of 592 cases (51.9%).
Conclusions
The incidence of VRI in our cohort was comparable to what has previously been reported. Coagulase-negative staphylococci was the most common agent. Our study demonstrates the difficulty in diagnosing VRI in SAH patients. Improved adherence to clinical guidelines could to some extent reduce the use of empirical antibiotic treatment, but better diagnostic methods and routines are needed.
Related collections
Most cited references36
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Coagulase-negative staphylococci.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Relation of cerebral vasospasm to subarachnoid hemorrhage visualized by computerized tomographic scanning.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found