- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Prediction kinetic, energy and exergy of quince under hot air dryer using ANNs and ANFIS

Read this article at
Abstract
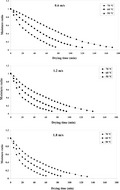
This study aimed to predict the drying kinetics, energy utilization ( E u ), energy utilization ratio ( EUR), exergy loss, and exergy efficiency of quince slice in a hot air (HA) dryer using artificial neural networks and ANFIS. The experiments were performed at air temperatures of 50, 60, and 70°C and air velocities of 0.6, 1.2, and 1.8 m/s. The thermal parameters were determined using thermodynamic relations. Increasing air temperature and air velocity increased the effective moisture diffusivity ( D eff ), E u , EUR, exergy efficiency, and exergy loss. The value of the D eff was varied from 4.19 × 10 –10 to 1.18 × 10 –9 m 2/s. The highest value E u , EUR, and exergy loss and exergy efficiency were calculated 0.0694 kJ/s, 0.882, 0.044 kJ/s, and 0.879, respectively. Midilli et al. model, ANNs, and ANFIS model, with a determination coefficient ( R 2) of .9992, .9993, and .9997, provided the best performance for predicting the moisture ratio of quince fruit. Also, the ANFIS model, in comparison with the artificial neural networks model, was better able to predict E u , EUR, exergy efficiency, and exergy loss, with R 2 of .9989, .9988, .9986, and .9978, respectively.
Abstract
In this study, drying kinetics, effective moisture diffusivity (Deff), activation energy (Ea), specific energy consumption (SEC), energy utilization (Eu), energy utilization ratio (EUR), exergy loss, and exergy efficiency in a hot air (HA) dryer are presented for quince fruit slices. Midilli et al. model, ANNs, and ANFIS model, with a determination coefficient ( R 2) of .9992, .9993, and 0.9997 provided the best performance for predicting the moisture ratio of quince fruit. Also, the ANFIS model in comparison with the artificial neural network model was better able to predict Eu, EUR, exergy efficiency, and exergy loss, with the R 2 of .9989, .9988, .9986, and .9978, respectively.
Related collections
Most cited references68
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
Convective drying of hawthorn fruit (Crataegus spp.): Effect of experimental parameters on drying kinetics, color, shrinkage, and rehydration capacity
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Recent developments of artificial intelligence in drying of fresh food: A review
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found