- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Inflammatory Bowel Disease Transcriptome and Metatranscriptome Meta-Analysis (IBD TaMMA) framework
Read this article at
Abstract
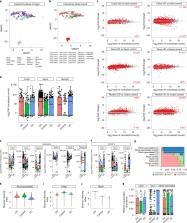
Inflammatory bowel disease (IBD) is a class of chronic disorders whose etiogenesis is still unknown. Despite the high number of IBD-related omics studies, the RNA-sequencing data produced results that are hard to compare because of the experimental variability and different data analysis approaches. We here introduce the IBD Transcriptome and Metatranscriptome Meta-Analysis (TaMMA) framework, a comprehensive survey of publicly available IBD RNA-sequencing datasets. IBD TaMMA is an open-source platform where scientists can explore simultaneously the freely available IBD-associated transcriptomics and microbial profiles thanks to its interactive interface, resulting in a useful tool to the IBD community.
Abstract
Massimino et al. propose the Inflammatory Bowel Disease Transcriptome and Metatranscriptome Meta-Analysis (IBD TaMMA) framework, an open-source platform for expediting the investigation of IBD-specific transcriptomics and metatranscriptomics signatures.
Related collections
Most cited references32

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found