- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
A Serpin With a Finger in Many PAIs: PAI-1's Central Function in Thromboinflammation and Cardiovascular Disease
Read this article at
Abstract
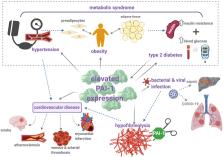
Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 (PAI-1) is a member of the serine protease inhibitor (serpin) superfamily. PAI-1 is the principal inhibitor of the plasminogen activators, tissue plasminogen activator (tPA), and urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA). Turbulence in the levels of PAI-1 tilts the balance of the hemostatic system resulting in bleeding or thrombotic complications. Not surprisingly, there is strong evidence that documents the role of PAI-1 in cardiovascular disease. The more recent uncovering of the coalition between the hemostatic and inflammatory pathways has exposed a distinct role for PAI-1. The storm of proinflammatory cytokines liberated during inflammation, including IL-6 and TNF-α, directly influence PAI-1 synthesis and increase circulating levels of this serpin. Consequently, elevated levels of PAI-1 are commonplace during infection and are frequently associated with a hypofibrinolytic state and thrombotic complications. Elevated PAI-1 levels are also a feature of metabolic syndrome, which is defined by a cluster of abnormalities including obesity, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and elevated triglyceride. Metabolic syndrome is in itself defined as a proinflammatory state associated with elevated levels of cytokines. In addition, insulin has a direct impact on PAI-1 synthesis bridging these pathways. This review describes the key physiological functions of PAI-1 and how these become perturbed during disease processes. We focus on the direct relationship between PAI-1 and inflammation and the repercussion in terms of an ensuing hypofibrinolytic state and thromboembolic complications. Collectively, these observations strengthen the utility of PAI-1 as a viable drug target for the treatment of various diseases.
Related collections
Most cited references212
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
The Global Epidemic of the Metabolic Syndrome
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found
The metabolic syndrome—a new worldwide definition
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found