- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Activated Yes-Associated Protein Accelerates Cell Cycle, Inhibits Apoptosis, and Delays Senescence in Human Periodontal Ligament Stem Cells
Read this article at
Abstract
Objectives: To provide insight into the biological effects of activated Yes-associated protein (YAP) on the proliferation, apoptosis, and senescence of human periodontal ligament stem cells (h-PDLSCs).
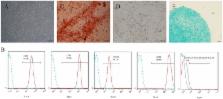
Methods: h-PDLSCs were isolated by the limiting dilution method, and their surface markers were quantified by flow cytometry. Enhanced green fluorescence protein (EGFP)-labeled lentiviral vector was used to activate YAP in h-PDLSCs, then qRT-PCR and Western blotting were used to evaluate the expression level of YAP. Immunofluorescence was used to detect the location of YAP in h-PDLSCs. The proliferation activity was detected by cell counting kit-8 (CCK-8) and 5-ethynyl-2'-deoxyuridine (EdU), and the cell cycle was determined by flow cytometry. Apoptosis was analyzed by Annexin V-APC staining. Cell senescence was detected by β-galactosidase staining. Proteins in ERK, Bcl-2, and p53 signaling pathways were detected by Western blotting.
Results: h-PDLSCs were isolated successfully and were positive for human mesenchymal stem cell surface markers. After YAP was activated by lentiviral vector, the mRNA and protein of YAP were highly expressed, and more YAP translocated into the nucleus. When YAP was overexpressed in h-PDLSCs, proliferation activity was improved; early and late apoptosis rates decreased (P<0.05); the proportion of cells in G2/M phases increased (P<0.05), while that in G0/G1 phase decreased (P<0.05); cellular senescence was delayed (P<0.01); the expression of P-MEK, P-ERK, P-P90RSK and P-Msk increased, while the expression of Bcl-2 family members (Bak, Bid and Bik) decreased.
Conclusions: Activated YAP promotes proliferation, inhibits apoptosis, and delays senescence of h-PDLSCs. The Hippo-YAP signaling pathway can influence ERK and Bcl-2 signaling pathways.
Related collections
Most cited references30
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Hippo signaling: growth control and beyond.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Snail/Slug-YAP/TAZ Complexes Control Skeletal Stem Cell Self-Renewal and Differentiation
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found