- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Comprehensive strategies of machine-learning-based quantitative structure-activity relationship models

Read this article at
Summary
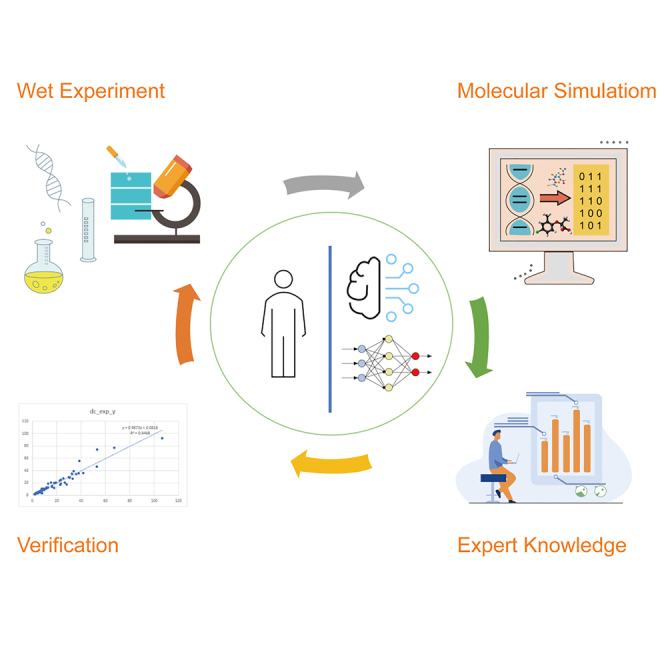
Early quantitative structure-activity relationship (QSAR) technologies have unsatisfactory versatility and accuracy in fields such as drug discovery because they are based on traditional machine learning and interpretive expert features. The development of Big Data and deep learning technologies significantly improve the processing of unstructured data and unleash the great potential of QSAR. Here we discuss the integration of wet experiments (which provide experimental data and reliable verification), molecular dynamics simulation (which provides mechanistic interpretation at the atomic/molecular levels), and machine learning (including deep learning) techniques to improve QSAR models. We first review the history of traditional QSAR and point out its problems. We then propose a better QSAR model characterized by a new iterative framework to integrate machine learning with disparate data input. Finally, we discuss the application of QSAR and machine learning to many practical research fields, including drug development and clinical trials.
Graphical abstract
Abstract
Data analysis in structural biology; Machine learning; Structural biology
Related collections
Most cited references256
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Deep learning.
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading.
- Record: found
- Abstract: not found
- Article: not found