- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Review targeted drug delivery systems for norcantharidin in cancer therapy

Read this article at
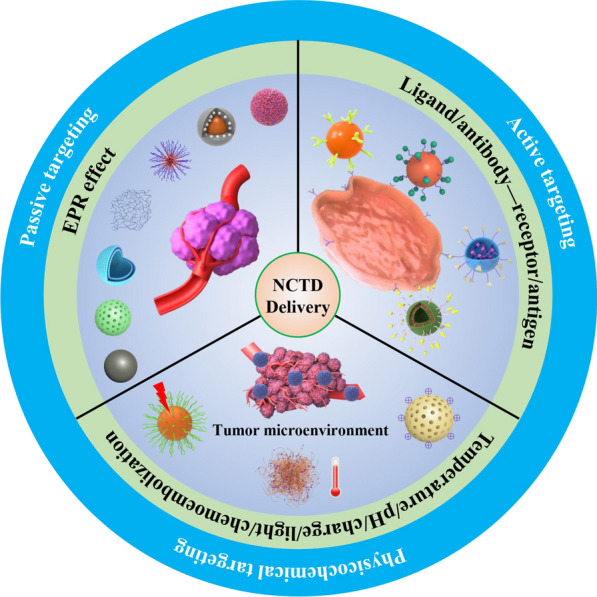
Abstract
Norcantharidin (NCTD) is a demethylated derivative of cantharidin (CTD), the main anticancer active ingredient isolated from traditional Chinese medicine Mylabris. NCTD has been approved by the State Food and Drug Administration for the treatment of various solid tumors, especially liver cancer. Although NCTD greatly reduces the toxicity of CTD, there is still a certain degree of urinary toxicity and organ toxicity, and the poor solubility, short half-life, fast metabolism, as well as high venous irritation and weak tumor targeting ability limit its widespread application in the clinic. To reduce its toxicity and improve its efficacy, design of targeted drug delivery systems based on biomaterials and nanomaterials is one of the most feasible strategies. Therefore, this review focused on the studies of targeted drug delivery systems combined with NCTD in recent years, including passive and active targeted drug delivery systems, and physicochemical targeted drug delivery systems for improving drug bioavailability and enhancing its efficacy, as well as increasing drug targeting ability and reducing its adverse effects.
Related collections
Most cited references233
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found
Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries

- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: found
Progress and challenges towards targeted delivery of cancer therapeutics
- Record: found
- Abstract: found
- Article: not found